Hydrothermal-derived black carbon
as a source of recalcitrant dissolved organic carbon in the ocean
作者:Youhei Yamashita, Yutaro Mori, Hiroshi Ogawa
期刊:Science Advances
Deep-sea hydrothermal vents are a possible source of thermogenic dissolved black carbon (DBC), which is a component of recalcitrant dissolved organic carbon, but little is known about the distribution of hydrothermal DBC in the deep ocean. Here, we show basin-scale distributions of DBC along two transects in the eastern Pacific Ocean, which are located outside the jet-like hydrothermal plumes from the East Pacific Rise. The DBC concentration in the deep waters did not show a strong linear relationship with apparent oxygen utilization (AOU), as previously observed in the central and western Pacific Ocean. Deviations in DBC concentration from the DBC-AOU relationship observed in the central and western Pacific Ocean were quantified. The deviation was linearly correlated with excess 3He, a tracer for hydrothermal input, indicating that a fraction of the DBC in the deep ocean is transported long distances from hydrothermal systems.
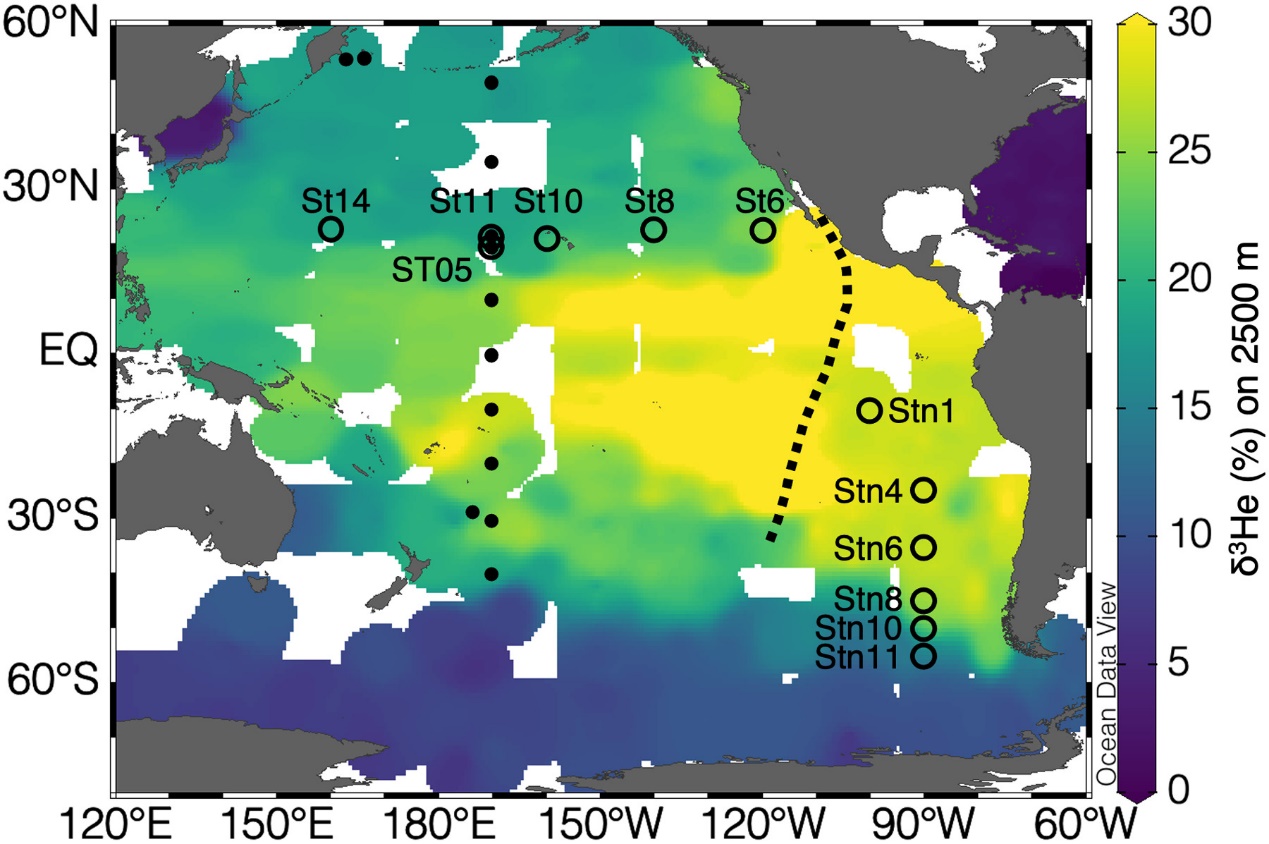
Figure. 1 Spatial distribution of δ3He values at a depth of approximately 2500 m and the sampling sites. The δ3He data were derived from Jenkins et al. (30). The open circles are sampling sites with site numbers in the present study along a zonal transect in the subtropical North Pacific Ocean and a meridional transect in the eastern South Pacific Ocean. The closed circles are sampling sites from Yamashita et al. (16), which determined the linear relationship between the DBC concentration and AOU in the central and western Pacific Ocean. The black dashed line shows the position of the EPR axis (37). Two major helium jets extend westward from the EPR axis at 10°N and at 15°S (37).
热成因的溶解性黑碳(DBC)是惰性溶解有机碳中的一种,深海热液喷口是这种DBC的一大可能来源,但是人们对热液成因的DBC在深海中的分布知之甚少。本文展示了东太平洋两个横断面上DBC在洋盆尺度的分布,这些横断面位于东太平洋洋隆上喷射状热液羽流的之外。东太平洋深海DBC浓度与表观耗氧量(AOU)没有明显的线性相关性,这与之前在太平洋中部和西太平洋观察到的不同。,通过对太平洋中部和西部观测到的DBC-AOU相互关系中DBC浓度偏差的量化分析发现,这一偏差与过量的3He(热液输入的示踪剂)呈线性关系,这表明深海中一部分DBC是从热液系统中经过长距离输送过来的。
(实习生江薇编译)








